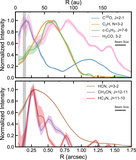
Image Details
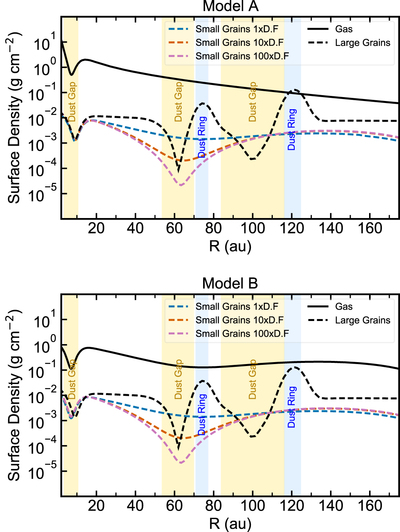
Caption: Figure 1.
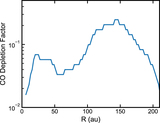
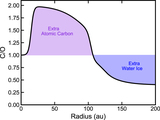
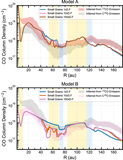
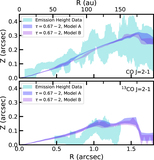
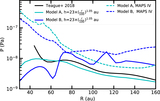
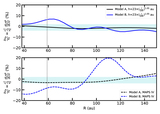
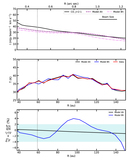
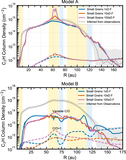
Two sets of models with varying surface density for the small grains. The small-grain surface density was changed by varying the depletion in the 59 au gap with three different depletion factors, 1× (nominal), 10× and 100×. Top: In Model A, the surface density has no gas substructures, i.e., it follows a smooth H2 surface-density profile, where CO is not a H2 mass tracer. Bottom: Model B, showing the surface density using the CO structure as a H2 gas mass tracer, scaling with a constant CO abundance. Model B shows a wide gas gap at 59 au. The shaded areas in yellow and blue are the dust gaps and dust ring, respectively.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2021. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.