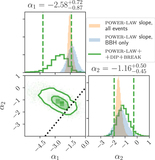
Image Details
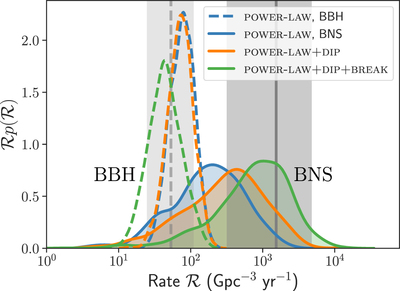
Caption: Figure 7.
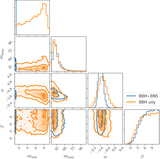
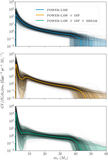
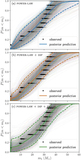
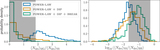
Astrophysical merger rate within two different mass bins: for BNS, 1 M⊙ < m2 < m1 < 2.5 M⊙, and for BBH, 5 M⊙ < m2 < m1 < 100 M⊙, as inferred by each of the models. The dashed open probability density curves centered below ﹩{ \mathcal R }\sim {10}^{2}\,\ {\mathrm{Gpc}}^{-3}\ {\mathrm{yr}}^{-1}﹩ show the BBH rate inference and the solid filled curves show the BNS rate inference for the POWER LAW (blue), POWER LAW + DIP (orange), and POWER LAW + DIP + BREAK (green) models. For comparison, the gray shaded regions show the median and 90% credible intervals of the BBH (dashed) and BNS (solid) rates inferred by the LVC in Abbott et al. (2019a, 2019b). Allowing for a dip and break between NS and BH masses tends to decorrelate the merger rates, increasing the inferred BNS merger rate and decreasing the BBH merger rate.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2020. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.