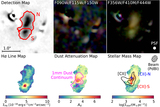
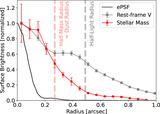
Image Details
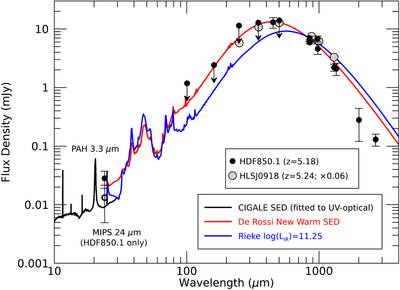
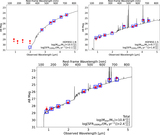
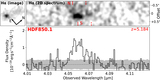
Caption: Figure 4.
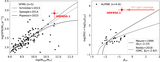
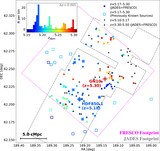
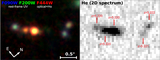
Far-IR (rest-frame) photometry of HDF850.1. The measurements are from Cowie et al. (2009; 24 μm; the empty circle shows the HDF850.1-only flux density of 13 μJy), Walter et al. (2012; 100–500 μm and 0.98/2.7 mm), Cowie et al. (2017; 450 μm), Hughes et al. (1998; 850 μm, 1.35 mm), Chapin et al. (2009; 850 μm; the measurement at 1.1 mm is not plotted because of its low signal to noise), Neri et al. (2014; 980 μm), Downes et al. (1999; 1.3 mm), and Staguhn et al. (2014; 2 mm). The SED templates (scaled to the 850 μm points) are from Rieke et al. (2009; blue line) and the newly derived warm SED template preferred for the redshift of HDF850.1 (red line). The latter is broadly consistent with the measured SED shape of the bright lensed galaxy HLSJ0918 at z = 5.24 (Rawle et al. 2014). The 24 μm points have an error bar determined by combining the statistical error and expected confusion noise by root sum square; for the 100, 160, 250, 350, and 500 μm points, the 2σ upper limits from Walter et al. (2012) are shown. The best-fit CIGALE SED for the whole system is also plotted up to 30 μm (black line). Please refer to Walter et al. (2012) for a far-IR SED model fit based on a modified blackbody using the MAGPHYS program (da Cunha et al. 2008).
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2024. The Author(s). Published by the American Astronomical Society.