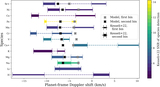
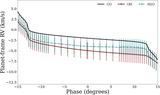
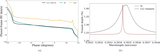
Image Details
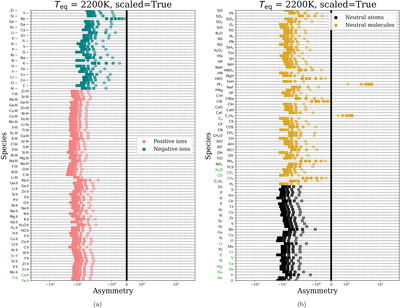
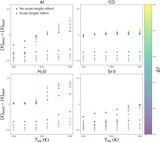
Caption: Figure 2.
Similar to Figure 1, but now including the scale height effect (inflating the hotter limb in our parameterized models). Now, all species have asymmetries that favor the hotter limb (negative asymmetry)—simply because the hotter limb subtends more solid angle on the sky. However, there still exists inter-species variability in asymmetry, implying that the scale height effect does not entirely swamp genuine differences in equilibrium chemistry across limbs. Furthermore, negative ions still have larger asymmetries than positive ions or neutral species.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2023. The Author(s). Published by the American Astronomical Society.