Image Details
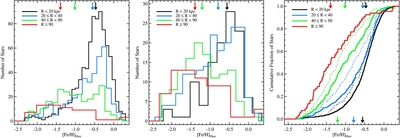
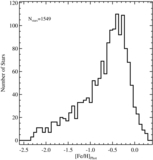
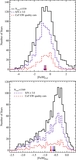
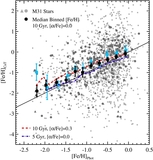
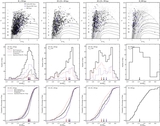
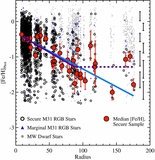
Caption: Figure 8.
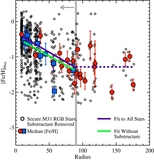
MDFs of the four radial regions shown separately in Figure 7, in differential (left: all M31 stars; middle: excluding kinematically cold substructure) and cumulative (right) form. Arrows mark the median metallicity of each distribution. As projected distance from M31 increases, the stellar population becomes increasingly dominated by metal-poor stars ([Fe/H]phot<−1.0), and the median metallicity of the population decreases significantly, irrespective of whether or not tidal debris features are included. The cumulative diagram directly compares the MDF of M31's stellar halo including (solid curves; top arrows) and excluding (dashed curves; bottom arrows) kinematically cold substructure. The difference between the MDFs of adjacent radial bins becomes more pronounced when tidal debris features are removed. The MDF of the kinematically hot population in the 40 ⩽ Rproj <90 kpc approaches the MDF of the Rproj ⩾90 kpc bin.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2014. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.