Image Details
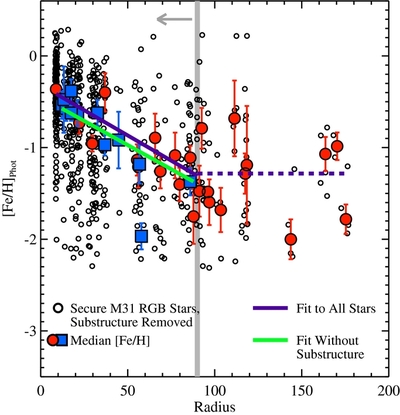
Caption: Figure 10.
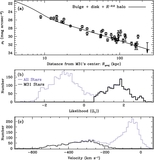
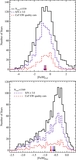
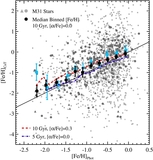
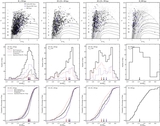
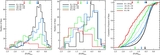
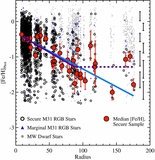
Similar to Figure 9, but showing only M31 halo stars that are not associated with kinematically distinct tidal debris features. In fields with kinematically identified substructure, only stars more than 3σv, kcc removed from the mean velocity of kinematic substructures are included (Section 4.1.1); the median [Fe/H] values for these fields are shown as large blue squares. Beyond Rproj =90 kpc, our spectroscopic fields have too few stars to kinematically identify tidal debris features; this boundary is marked by the light gray line and arrow. The green line shows the linear least-squares fit to the median [Fe/H] values in fields with 10 < Rproj <90 kpc (Section 4.2.1). As in Figure 9, the purple line shows the fit to the median [Fe/H] values when all M31 stars are included, while the purple dashed line shows the median [Fe/H] of all M31 stars with Rproj >90 kpc. When substructure is included the median metallicity of fields within 10 ⩽ Rproj ⩽30 kpc is approximately constant (Figure 9); once substructure is removed, the fields within this radial range are consistent with the observed large-scale gradient.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2014. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.