Image Details
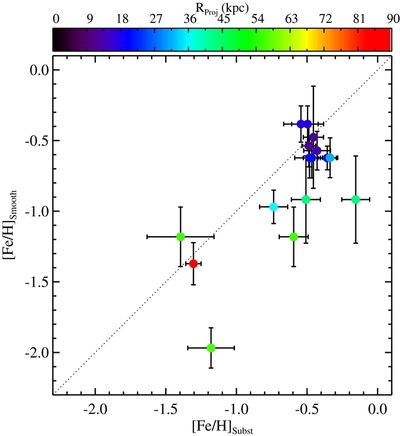
Caption: Figure 13.
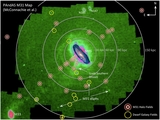
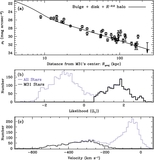
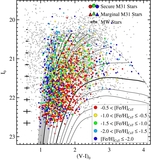
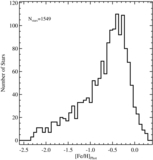
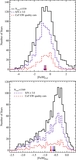
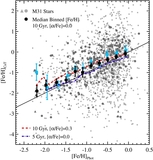
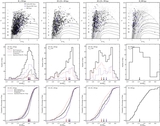
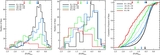
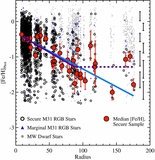
Comparison of the median metallicity of stars associated with each kinematically identified cold tidal debris feature and stars associated with the comparatively smooth, kinematically hot stellar component in individual lines of sight in M31's stellar halo. Error bars show the error in the median value of each field. Points are color-coded by the field's mean projected distance from M31's center. The dotted line shows the one-to-one line. The majority of tidal debris features have a higher median metallicity than the spatially diffuse halo in the same location, even though most of the kinematically identified substructure is found in fields within ~35 kpc of M31's center, where the metallicity of the dynamically hot population is relatively high. The largest differences between the median metallicity of stars associated with the kinematically hot stellar population and the kinematically cold substructure is seen in fields at larger radius.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2014. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.