Image Details
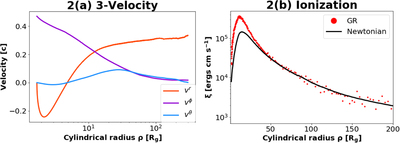
Caption: Figure 2.
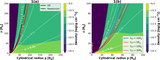
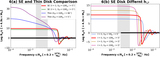
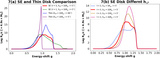
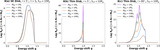
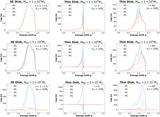
(a) The equivalent Newtonian three velocity of the gas along the reflection surface. The wind accelerates quickly and the outflowing motion dominates over rotation starting from ρ ≈ 10 Rg, after which the wind quickly reaches a terminal radial velocity of about 0.3c. (b) The ionization parameter ξ along the reflection surface. By accounting for the GR effects (red dotted curve), ξ is a few times larger in the inner disk region as compared to that obtained using Newtonian calculations (black thin curve).
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2022. The Author(s). Published by the American Astronomical Society.