Image Details
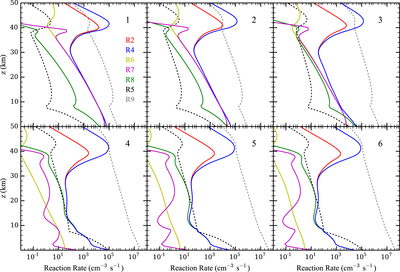
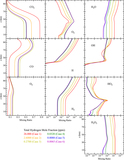
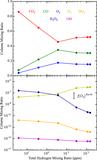
Caption: Figure 5.
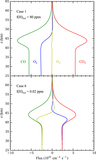
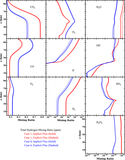
Reaction rates of R2: ﹩{{\rm H}}+{{{\rm O}}}_{2}+{{\rm M}}\to {\mathrm{HO}}_{2}+{{\rm M}}﹩ (red), R4: ﹩\mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{CO}\to {\mathrm{CO}}_{2}+{{\rm H}}﹩ (blue), R5: ﹩\mathrm{CO}+{{\rm O}}+{{\rm M}}\to {\mathrm{CO}}_{2}+{{\rm M}}﹩ (black, dotted line), R6: ﹩{{{\rm H}}}_{2}{{{\rm O}}}_{2}+{hv}\to 2\mathrm{OH}﹩ (yellow), R7: ﹩2{\mathrm{HO}}_{2}\to {{{\rm H}}}_{2}{{{\rm O}}}_{2}+{{{\rm O}}}_{2}﹩ (magenta), R8: ﹩{\mathrm{HO}}_{2}+{{{\rm O}}}_{3}\to 2{{{\rm O}}}_{2}+\mathrm{OH}﹩ (green), and R9: ﹩{{{\rm O}}}_{3}+{hv}\to {{{\rm O}}}_{2}+{{\rm O}}﹩ (gray, dotted line) as functions of altitude in the lower atmosphere for (1) Case 1, f(H)tot ∼ 26 ppm; (2) Case 2, f(H)tot ∼ 2.6 ppm; (3) Case 3, f(H)tot ∼ 0.27 ppm; (4) Case 4, f(H)tot ∼ 0.032 ppm; (5) Case 5, f(H)tot ∼ 0.0088 ppm; and (6) Case 6, f(H)tot ∼ 0.0065 ppm.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2015. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.