Image Details
Caption: Figure 1.
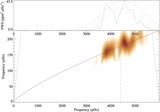
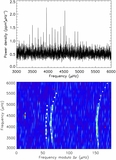
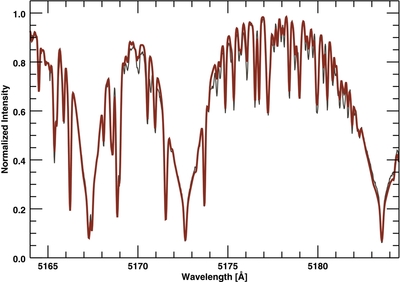
Observed and synthetic spectra in the wavelength region occupied by the Mg I b triplet lines. The spectral fitting procedure covered 160 Å with most of the coverage in the range 6000–6200 Å, while having also included the region around the gravity-sensitive Mg I b triplet lines. The synthetic spectrum (thick line) provides a good fit to the Mg I b line wings. The combined effect of rotational line broadening and macroturbulence takes a value of ~2.2 km s−1, an indication that this star is a fairly slow rotator.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2015. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.