Image Details
Caption: Figure 7.
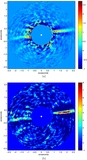
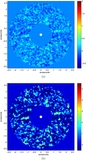
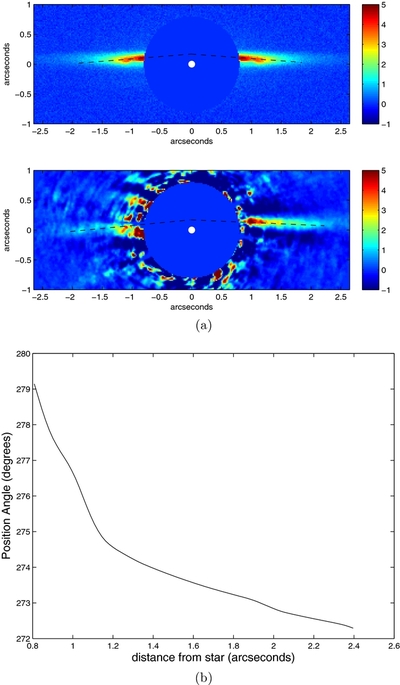
(a) Rotated model and real
Ks-band disk images. The model image has an inclination of 87°, scattering parameter
g = 0.5, 3 μm grains, an SB power-law index of −3/2, and a gap from 0 to 1
![]() 1. The model image has been convolved with the PSF from the photometric image of HBC 388, and Gaussian noise has been added.
Units are in mJy arcsec
−2 for both images. The white dot marks the location of the star in both images. The dashed lines are meant to guide the eye
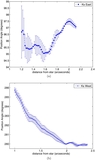
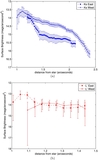
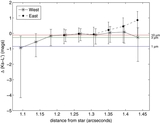
to the apparent northern offset of the disk relative to the star. (b) P.A. vs. stellocentric distance for the western side
of the disk in the model image. The P.A. increases closer to the star due to the apparent bow shape, similar to what is seen
for the real data shown in Figure
4(b).
1. The model image has been convolved with the PSF from the photometric image of HBC 388, and Gaussian noise has been added.
Units are in mJy arcsec
−2 for both images. The white dot marks the location of the star in both images. The dashed lines are meant to guide the eye
to the apparent northern offset of the disk relative to the star. (b) P.A. vs. stellocentric distance for the western side
of the disk in the model image. The P.A. increases closer to the star due to the apparent bow shape, similar to what is seen
for the real data shown in Figure
4(b).
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2012. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.