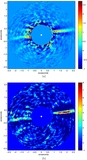
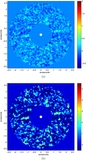
Image Details
Caption: Figure 10.
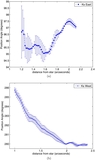
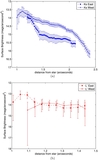
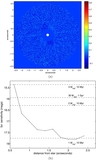
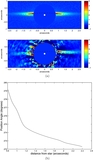
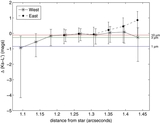
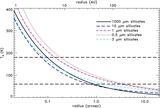
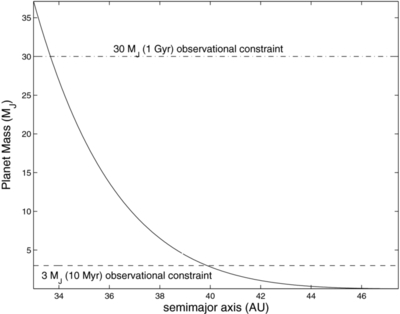
Masses of a possible object orbiting inside a disk gap with its outer edge at 1
![]() 1 (50 AU), as a function of semimajor axis, computed using Equation (1) (solid line). The dashed line represents our 3
M
J
(10 Myr old age) observational constraint and assumes that the planet's semimajor axis = its projected separation at the
epoch of our observations. The dash-dot line is the same, except showing our 30
M
J
(1 Gyr old age) observational constraint. If HD 15115 is old, then the object creating the gap must reside between ~34 and
45 AU. If the system is young, the allowed semimajor axis range shrinks to 40–45 AU.
1 (50 AU), as a function of semimajor axis, computed using Equation (1) (solid line). The dashed line represents our 3
M
J
(10 Myr old age) observational constraint and assumes that the planet's semimajor axis = its projected separation at the
epoch of our observations. The dash-dot line is the same, except showing our 30
M
J
(1 Gyr old age) observational constraint. If HD 15115 is old, then the object creating the gap must reside between ~34 and
45 AU. If the system is young, the allowed semimajor axis range shrinks to 40–45 AU.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2012. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.