Image Details
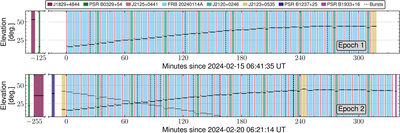
Caption: Figure 6.
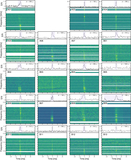
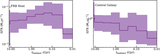
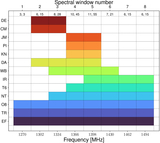
Observational timeline and calibration strategy for epoch 1 (top panel; PR318A/EK056A) and epoch 2 (bottom panel; PR319A/EK056B). The ∼6 minute target scans on FRB 20240114A are interleaved with ∼2 minute scans on the phase calibrator J2125+0441. Roughly twice per hour, the check source, J2120+0246, was observed for ∼3.5 minutes per scan to verify the astrometric calibration. Other sources include J1829+4844 and J2123+0535, which are used as fringe finders and bandpass calibrators, and various pulsars to test the data quality, frequency setup, and burst search pipeline. The solid horizontal black bars indicate the source elevation for the Effelsberg telescope (Germany), and the dashed horizontal gray bars indicate the same for the Tianma telescope (China). Vertical black dashed lines indicate the arrival times of the bursts. Vertical white bars indicate that the telescopes are slewing (slewing/on-source times are shown for Effelsberg, which is the slowest slewing antenna in the array).
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2025. The Author(s). Published by the American Astronomical Society.