Image Details
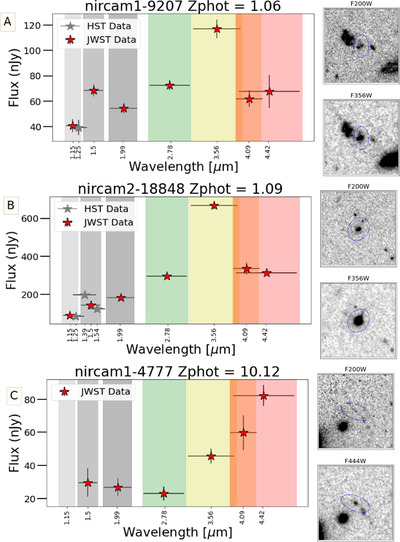
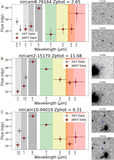
Caption: Figure 8.
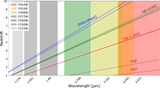
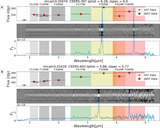
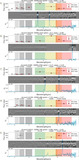
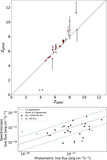
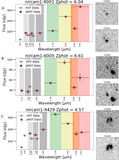
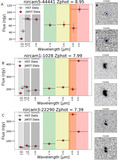
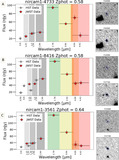
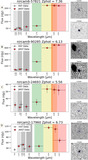
Examples of EELGs in confidence Tier 2B, with only one extreme emission feature (Hβ + [O III]) identified in a filter that is inconsistent with the SED-derived photometric redshift. Photometry postage stamps show a continuum filter (top) and an extreme emission filter (bottom), with north up and east left. All postage stamps are 4″ in width and height. Panel (A): extreme emission in F356W consistent with Hβ + [O III] at z ≈ 6.5. Panel (B): extreme emission in F356W consistent with Hβ + [O III] at z ≈ 6.5. The morphology exhibits a significant size difference between the continuum and emission filters, suggesting the presence of an extended ionization region. Panel (C): emission in F444W consistent with Hβ + [O III]. The SED shape is similar to extremely red objects reported by Barro et al. (2024), with a combination of a flat continuum in bluer filters and red emission in redder filters. The inferred Hβ + [O III] emission implies z < 9.5, inconsistent with the higher photometric redshift.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2024. The Author(s). Published by the American Astronomical Society.