Image Details
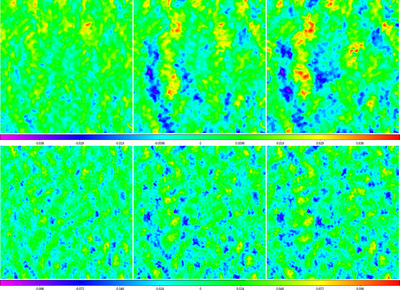
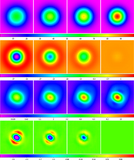
Caption: Figure 34.
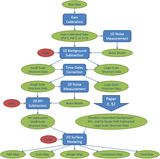
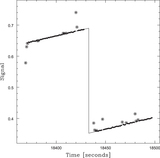
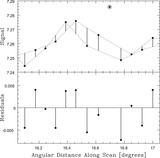
Data from the top row of Figure 14, corresponding to 6 (left column), 12 (middle column), and 24 (right column) beamwidth background-subtraction scales, RFI-subtracted, with 0.95 (top row) and 0.5 (bottom row) beamwidth scales. RFI-subtracted data are biased neither high nor low. On the 0.95 beamwidth scale, the noise level of the RFI-subtracted data is ≈1.1% (left), ≈1.3% (middle), and ≈1.4% (right) of that of the background-subtracted data. On the smaller, 0.5 beamwidth scale, the noise level of the RFI-subtracted data is roughly twice that, ≈2.5% (left), ≈2.8% (middle), and ≈3.0% (right) of that of the background-subtracted data. Locally modeled surfaces (Section 1.2.1, see Section 3.7) have been applied for visualization only.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2019. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.