Image Details
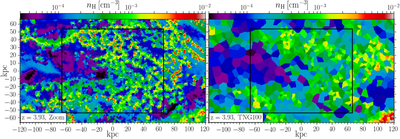
Caption: Figure 4.
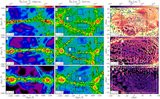
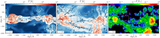
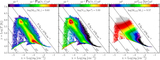
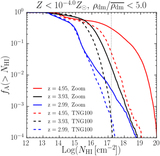
Shattering of the sheet due to thermal instability. We show an infinitesimally thin slice of the gas density near the midplane of the sheet at z = 4, in region F (as in Figure 3). The left panel shows our highest-resolution simulation, while the right panel shows a simulation with comparable resolution to TNG100. The typical cell size is ∼800 pc in the former and ∼4 kpc in the latter. The cooling length in the postshock medium, with T ≳ 105 K and nH ≲ 10−3 cm−3, is lcool ∼ 10 kpc. This is well resolved in our high-resolution simulation, which allows the shattering process to begin, but not in TNG100, which is why the resulting density distribution is much smoother, and in particular no LLSs are produced. An animation of the density distribution in the same two simulations, in infinitesimally thin slices separated by 1 kpc and moving up through the sheet from 30 kpc below the midplane to 30 kpc above it, is available. This figure represents a still frame of the animation in the midplane.
(An animation of this figure is available.)
The video/animation of this figure is available in the online journal.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2019. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.