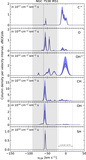
Image Details
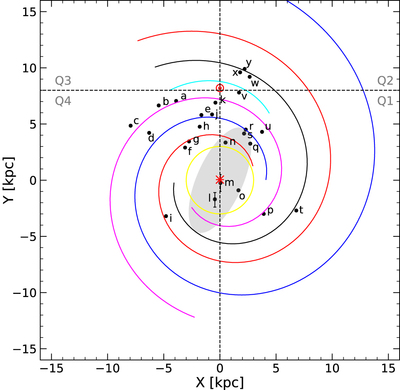
Caption: Figure 3.
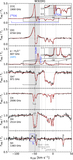
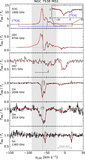
Distribution of the sight lines observed under the HyGAL program (black circles), as viewed from the north Galactic pole. The underlying trace of the Milky Way spiral arm pattern follows the log-periodic model presented in Reid et al. (2019); the Galactic center (red asterisk) is at (0, 0) kpc and the Sun (red Sun symbol) is at (0, 8.15) kpc; 3 kpc ring, yellow; Norma Outer arm, red; Scutum–Centaurus OSC arm, blue; Sagittarius–Carina arm, purple; Local arm, cyan; Perseus arm, black; the “long” bar is indicated by a shaded ellipse after Wegg et al. (2015). The source names are designated using alphabetic letters (as given in Table 2) for clarity, five of which are located in the outer Galaxy. The sources labeled as l and m in this plot are depicted using bars due to uncertainties in their kinematic distances. In this paper, we discuss sources labeled w, x, and y, respectively.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2022. The Author(s). Published by the American Astronomical Society.