Image Details
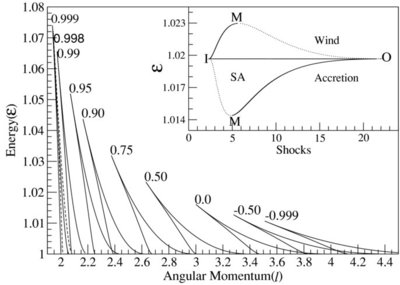
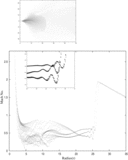
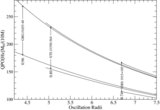
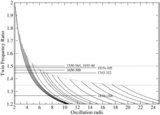
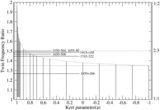
Caption: Figure 2.
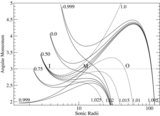
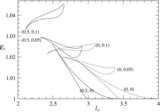
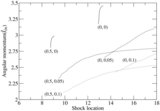
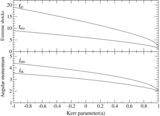
Classification of parameter space spanned by the specific energy and angular momentum responsible for "shocks in accretion" (SA) flows for different values of spin( a) is shown. The range of energy in a rapidly rotating black hole is much higher compared to that around a non-rotating black hole. But the span of angular momentum( l) shrinks and shifts to the lower values with the increase of spin. In the sub-panel, stable (solid) and unstable (dashed) shock locations are plotted in accretion (SA) and winds (SW) as a function of the specific energy of the flow for l = 2.313, a = 0.9. Stable shock location increases with the specific energy and extremum occurs at the middle sonic point M on the SA curve.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2010. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.