Image Details
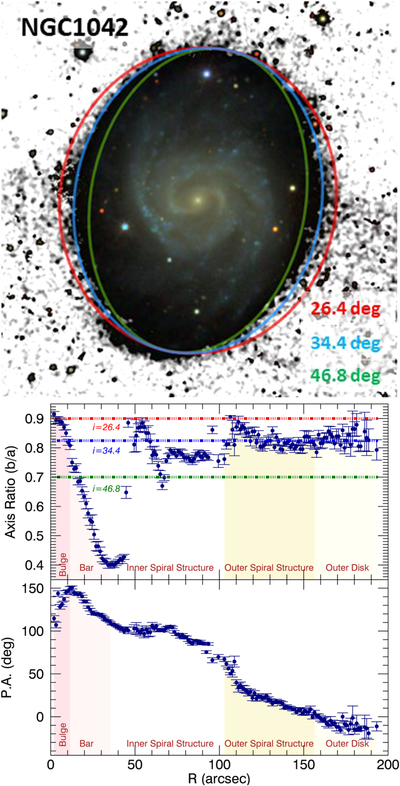
Caption: Figure 4.
Inclination of NGC 1042. Having an accurate estimation of the inclination of NGC 1042 is key to attaining a reliable measurement of the distance to the galaxy through the Tully–Fisher relation. The top panel shows the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) image of NGC 1042 with three elliptical contours overplotted with different axis ratio. The image is a color composite of the SDSS filters g, r, and i, being the black and white background the sum of all the filters. The blue line corresponds to the inclination 34.°4 that we measure in this work. Together with such an axis ratio, we show the corresponding ellipse representing the expected isophotal shape for an inclination of 26.°4 (b/a = 0.9; red line) and 46.°8 (b/a = 0.7; green line). For all cases we have assumed q0 = 0.2 (see the text for details). The lower panel shows the axis ratio and position angle profiles of NGC 1042 obtained with the IRAF ELLIPSE package. Inclinations lower than 30 degrees are not favored by the shape of the external isophotes of the galaxy. A distance of 19 Mpc would require b/a = 0.898 (i.e., 26.°7), which is ruled out by the observations.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2019. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.