Image Details
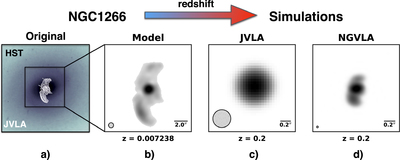
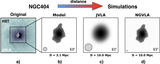
Caption: Figure 7.
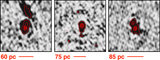
Simulated VLA and ngVLA images of a redshifted analog to the nearby jet-driven feedback candidate NGC 1266. (a) A near-infrared HST image (WFC3 F140W) from the Hubble Legacy Archive is shown in the background colorscale, and the VLA A-configuration radio contours at 5 GHz are overlaid in white. The angular resolution of the radio data is θFWHM = 0.″75, and the extent of the radio jets from end to end is 9.″5 (1.4 kpc). The NGC 1266 VLA data were originally published in Nyland et al. (2016). (b) Model radio image of NGC 1266 based on the original image shown in panel a) and shown at the true redshift of the source of z = 0.00728. (c) Simulated VLA A-configuration map of an NGC 1266 analog redshifted z = 0.2 at 5 GHz with θFWHM = 0.″34. (d) Simulated map of an NGC 1266 analog at z = 0.2 as it would appear if imaged with the ngVLA at 5 GHz. The angular resolution is θFWHM = 0.″03.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2018. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.