Image Details
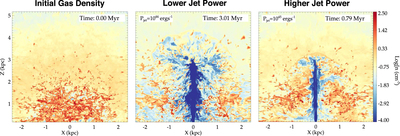
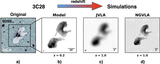
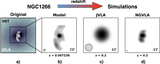
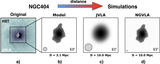
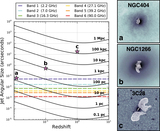
Caption: Figure 2.
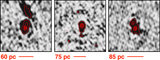
Snapshots from relativistic hydrodynamic radio jet simulations (Mukherjee et al. 2016, 2017) showing the impact on an identical initial ISM (left) by a radio jet with Pjet = 1044 erg s−1 (center) and Pjet = 1045 erg s−1 (right). The more powerful radio jet is able to more quickly “drill” through the ISM of its host galaxy, while the weaker radio jet is trapped by the ISM and disrupts the surrounding gas for a longer time period and over a larger volume.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2018. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.