Image Details
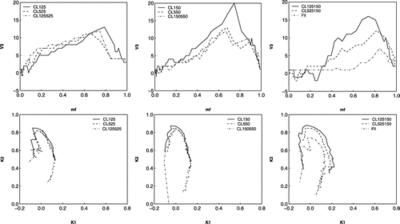
Caption: Fig. 14.
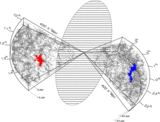
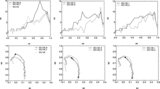
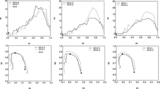
Euler characteristic (top panels) and the morphological signature ﹩K_{1}﹩‐﹩K_{2}﹩ (bottom panels) for the empirical models. Left panels: ﹩N_{\mathrm{cl}\,}=25﹩, ﹩N_{\mathrm{gal}\,}=20﹩, and the size of the clusters is 1 and 5 (in grid units), and the combined model where the centers of clusters coincide. Solid line: model CL125; dashed line: model CL525; dot‐dashed line: model CL125525. Middle panels: ﹩N_{\mathrm{cl}\,}=50﹩, ﹩N_{\mathrm{gal}\,}=10﹩, and the size of clusters is 1 and 5 (in grid units), and the combined model where the centers of clusters coincide. Solid line: model CL150; dashed line: model CL550; dot‐dashed line: model CL150550. Right panels: Combined models where the centers do not coincide. "Fil" denotes a simple filament with randomly distributed points. Solid line: model CL125150; dashed line: model CL525150; dot‐dashed line: model "Fil."
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.