Image Details
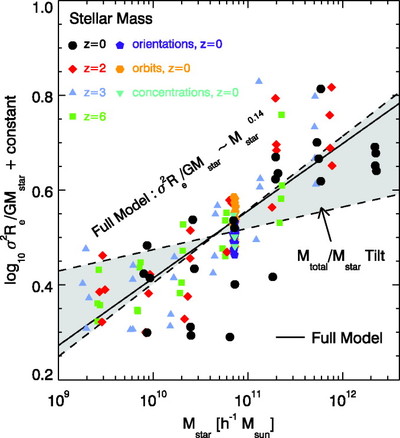
Caption: Fig. 16.
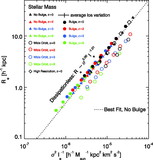
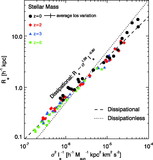
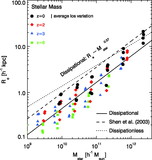
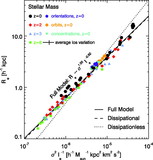
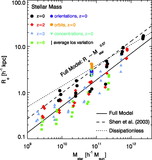
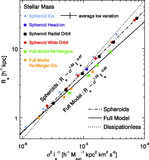
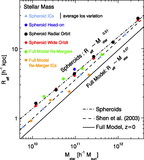
Ratio of the dynamical mass estimator ﹩M_{\mathrm{dyn}\,}\equiv \sigma ^{2}R_{e}/ G﹩ to the stellar mass M![]() in the full‐model simulations as a function of stellar mass for remnants of mergers between progenitor disk galaxies appropriate for redshifts ﹩z=0﹩ (black circles), ﹩z=2﹩ (red diamonds), ﹩z=3﹩ (blue triangles), and ﹩z=6﹩ (green squares). Also shown is the measured Mdyn/M
in the full‐model simulations as a function of stellar mass for remnants of mergers between progenitor disk galaxies appropriate for redshifts ﹩z=0﹩ (black circles), ﹩z=2﹩ (red diamonds), ﹩z=3﹩ (blue triangles), and ﹩z=6﹩ (green squares). Also shown is the measured Mdyn/M![]() for ﹩z=0﹩ mergers with varying disk orientations (purple pentagons), orbital parameters (orange hexagons), and dark matter concentrations (cyan triangles). The best‐fit trend ﹩M_{\mathrm{dyn}\,}/ M_{\star }\propto M^{0.14}_{\star }﹩ (solid line) recovers the complete FP tilt measured for the full‐model simulations in Fig. 5. We also estimate the tilt contributed by variations of Mtotal/M
for ﹩z=0﹩ mergers with varying disk orientations (purple pentagons), orbital parameters (orange hexagons), and dark matter concentrations (cyan triangles). The best‐fit trend ﹩M_{\mathrm{dyn}\,}/ M_{\star }\propto M^{0.14}_{\star }﹩ (solid line) recovers the complete FP tilt measured for the full‐model simulations in Fig. 5. We also estimate the tilt contributed by variations of Mtotal/M![]() averaged within an effective radius as a function of stellar mass measured from the remnant particle distribution (shaded area; see § 5.3.1), which contributes ≈40%–100% of the nonhomology‐related FP tilt. The Mtotal/M
averaged within an effective radius as a function of stellar mass measured from the remnant particle distribution (shaded area; see § 5.3.1), which contributes ≈40%–100% of the nonhomology‐related FP tilt. The Mtotal/M![]() tilt estimates shown have been renormalized by a constant to intersect with the best‐fit Mdyn/M
tilt estimates shown have been renormalized by a constant to intersect with the best‐fit Mdyn/M![]() relation at the same location.
relation at the same location.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.