Image Details
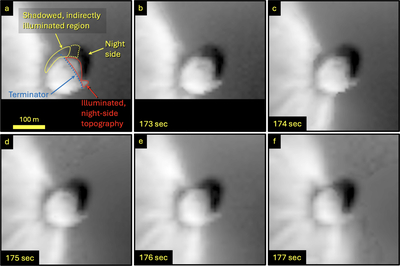
Caption: Figure 8.
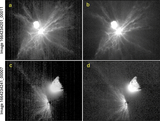
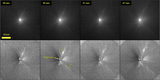
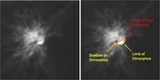
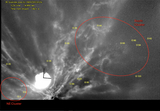
Temporal sequence of images with close-ups of Dimorphos after close approach. Features noted in the text are highlighted in panel (a) (173 s), including the illuminated nightside topography and the shadow along the top limb cast by the dense ejecta at the base of the cone. This shadowed region is somewhat brighter than the nightside owing to indirect illumination from the bright ejecta higher in the cone. (Note that this indirect illumination extends beyond the terminator.) Over time, the shadow also disappears over the horizon as the spacecraft moves from −40° to −26° latitude during the sequence. The images are displayed with a logarithmic display to more clearly reveal the illuminated nightside topography.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2025. The Author(s). Published by the American Astronomical Society.