Image Details
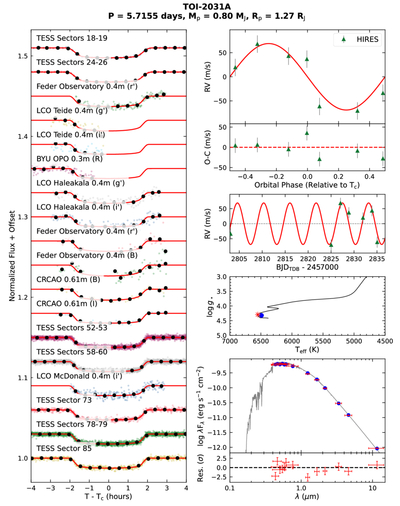
Caption: Figure 4. Data and EXOFASTv2 fit results
The complete figure set (30 images) is available in the online journal.
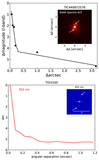
Data and EXOFASTv2 fit results for TOI-2031 b. Left: TESS and ground-based light curves, phase-folded onto the best-fit period and time of conjunction. Faint colored points represent the unbinned data, while large black circles show the time series data binned to a 30-minute cadence. The best-fit transit model in each band is shown as the red line. Top right: RV observations, also phased onto the best-fit orbital period. Error bars represent the fitted per-instrument jitter term σjit added in quadrature to the instrumental uncertainties. The red line shows the best-fit RV model. We plot the residuals after subtracting the model in the middle subpanel, and the unphased RV data and model time series in the lower subpanel. Middle right: the best-fit MIST stellar evolution track (black line), with a red asterisk marking the position along the track corresponding to the best-fit stellar age. The blue point represents the best-fit stellar Teff and ﹩{\mathrm{log}}\,g﹩. The discrepancy between the blue point and red asterisk is well within the fitted uncertainties in each parameter, indicating no tension between the different constraints on the stellar properties. Bottom right: The observed stellar fluxes from the Gaia, UCAC, 2MASS, and WISE catalogs are plotted in red, with horizontal error bars corresponding to the width of the photometric bandpass. The blue points show the best-fit model flux derived from the stellar properties and MIST bolometric correction grid. We plot in gray an atmospheric model from R. L. Kurucz (1993) corresponding to the best-fit stellar parameters for illustrative purposes only, as the fit is performed directly to the MIST grid. The TESS and ground-based time series photometry, as well as the RV measurements, are available as data behind the figure.
(The data used to create this figure are available in the online article.)
(The data used to create this figure are available.)
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2025. The Author(s). Published by the American Astronomical Society.