Image Details
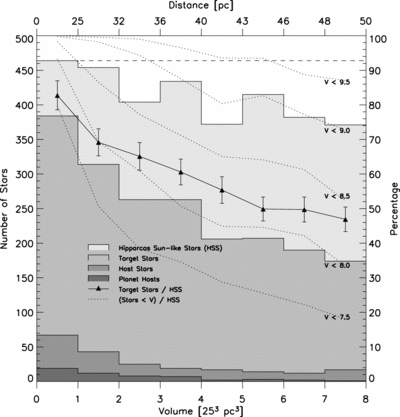
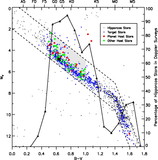
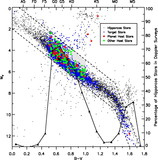
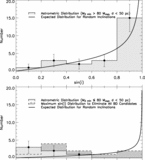
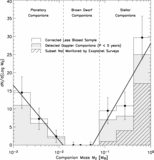
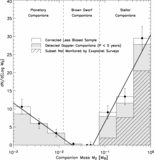
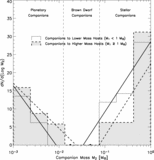
Caption: Fig. 4.
Distance dependence of sample and companions. Here we show the number of nearby Sun‐like stars as a function of distance. Each histogram bin represents the stars in an equal‐volume spherical shell. Hence, a sample that is complete in distance out to 50 pc would produce a flat histogram (horizontal dashed line). The lightest shade of gray represents Hipparcos Sun‐like Stars out to 50 pc that fall within the parallelogram of Fig. 2 ("HSS"). The next darker shade of gray represents Hipparcos stars that are being monitored for planets using the high‐precision Doppler techniques (eight groups described in Lineweaver & Grether 2003). The triangles represent this number as a fraction of Hipparcos stars. This fraction needs to be as large as possible to minimize distance‐dependent selection effects in the target sample potentially associated with companion frequency. Also shown (darker gray) are the number of Hipparcos stars that have one or more companions in the mass range ﹩10^{-3}< M/ M_{\odot }< 1﹩ and those that host planets (darkest gray). Only those companions in the less biased sample, ﹩P< 5﹩ yr and ﹩M_{2}> 10^{-3}\ M_{\odot }﹩, are shown (§ 2.2). The fraction of stars having an apparent V magnitude brighter (lower) than a given value are shown by the five dotted lines for ﹩V< 7.5{\mbox{--}} 9.5﹩.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.