Image Details
Caption: Figure 4.
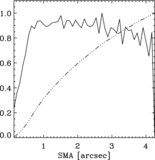
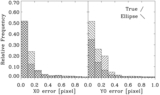
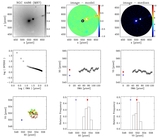
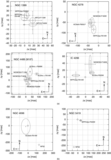
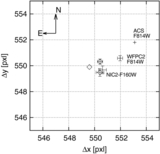
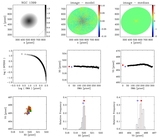
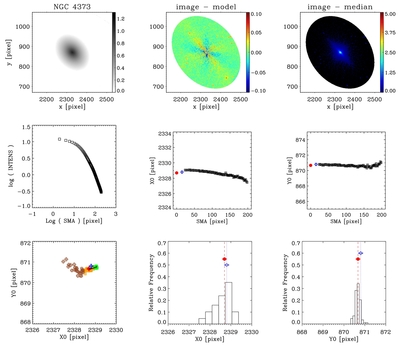
Example of a galaxy where the displacement is not significant. NGC 4373, WFPC2/PC-F814W, scale = 0![]() 05 pixel−1. First row, left to right: the galaxy log(counts s−1); note that the color scale is adjusted to highlight the presence of the nuclear point source, and emission is present over the whole field of view; galaxy after subtraction of the isophotal model; galaxy after subtraction of the median filter. Second row: surface-brightness profile in counts s−1; second and third panels: x and y coordinates of the isophotal centers vs. semimajor axis length. Blue diamond: AGN; red bullet: photocenter. The blue diamond and the red bullet are not positioned both at SMA = 0 to make the figure clear and avoid superpositions. Third row: scatter plot of the isophote centers. The solid line (near the photocenter) is the cumulative photocenter computed including progressively all data from the core radius outward. Different colors for the data points are used to represent the centers of isophotes with SMA length in a given range. Defining w = 33% (SMAmax − rc): green: rc < SMA ⩽ rc + w, orange: rc + w < SMA ⩽ rc + 2w, brown: rc + 2w < SMA < SMAmax. Second and third panels: histograms of the distributions of the x and y coordinates of the isophotal centers.
05 pixel−1. First row, left to right: the galaxy log(counts s−1); note that the color scale is adjusted to highlight the presence of the nuclear point source, and emission is present over the whole field of view; galaxy after subtraction of the isophotal model; galaxy after subtraction of the median filter. Second row: surface-brightness profile in counts s−1; second and third panels: x and y coordinates of the isophotal centers vs. semimajor axis length. Blue diamond: AGN; red bullet: photocenter. The blue diamond and the red bullet are not positioned both at SMA = 0 to make the figure clear and avoid superpositions. Third row: scatter plot of the isophote centers. The solid line (near the photocenter) is the cumulative photocenter computed including progressively all data from the core radius outward. Different colors for the data points are used to represent the centers of isophotes with SMA length in a given range. Defining w = 33% (SMAmax − rc): green: rc < SMA ⩽ rc + w, orange: rc + w < SMA ⩽ rc + 2w, brown: rc + 2w < SMA < SMAmax. Second and third panels: histograms of the distributions of the x and y coordinates of the isophotal centers.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2014. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.