Image Details

Caption: Figure 6.
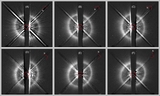
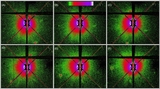
Smallest of the ACS coronagraphic masks (used in the HD 181327 scattered-light disk co-discovery imaging, panel (A)) provides r ⩽ 0![]() 9 IWA obscuration. However, ACS PSF-subtraction residuals completely dominate the disk light interior to the radius of the peak SB of the ring (r = 1
9 IWA obscuration. However, ACS PSF-subtraction residuals completely dominate the disk light interior to the radius of the peak SB of the ring (r = 1![]() 7) revealed by NICMOS PSFTSC (see Figure 1(B)) using various methods of different aggressiveness. The residuals seen in the ACS image are largely suppressed to much smaller stellocentric angles with STIS 6R/PSFTSC beyond the effective six-roll combined WedgeA-0.6 limiting, IWAeffective of r = 0
7) revealed by NICMOS PSFTSC (see Figure 1(B)) using various methods of different aggressiveness. The residuals seen in the ACS image are largely suppressed to much smaller stellocentric angles with STIS 6R/PSFTSC beyond the effective six-roll combined WedgeA-0.6 limiting, IWAeffective of r = 0![]() 3. Here, deeper (and better sampled) imaging of the outer portions of the disk with STIS 6R/PSFTSC (panel (B)) simultaneously provides high-fidelity, high-S/N imaging of the outer portions' low SB of the disk, the bright debris ring, and the largely cleared region in the ring interior. Both images: full FOV = 25'' × 25'', north up, east left.
3. Here, deeper (and better sampled) imaging of the outer portions of the disk with STIS 6R/PSFTSC (panel (B)) simultaneously provides high-fidelity, high-S/N imaging of the outer portions' low SB of the disk, the bright debris ring, and the largely cleared region in the ring interior. Both images: full FOV = 25'' × 25'', north up, east left.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2014. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved.