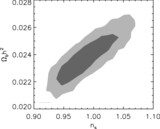
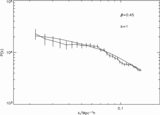
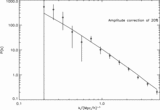
Image Details
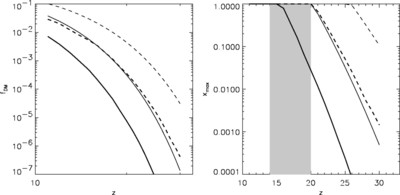
Caption: Fig. 7.
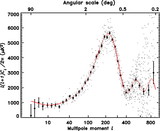
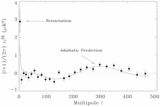
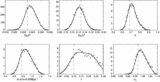
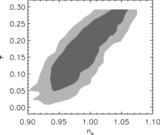
Left: Fraction of mass in bound objects as a function of redshift. The black lines show the mass in collapsed objects with mass greater than ﹩M^{\mathrm{HRL}\,}( z) ﹩, the effective Jeans mass in the absence of H2 cooling for our best‐fit PL ΛCDM model (thin lines are for the fit to WMAP only, and thick lines are for the fit to all data sets). The heavy line uses the best‐fit parameters based on all data (which has a lower σ8), and the light line uses the best‐fit parameters based on fitting to the WMAP data only. The dashed lines show the mass in collapsed objects with masses greater than the Jeans mass assuming that the minimum mass is 106 M⊙. More objects form if the minimum mass is lower. Right: Ionization fraction as a function of redshift. The solid line shows ionization fraction for the best‐fit PL ΛCDM model if we assume that H2 cooling is suppressed by photodestruction of H2. This figure suggests that H2 cooling may be necessary for enough objects to form early enough to be consistent with the WMAP detection. The heavy line is for the best‐fit parameters for all data sets, and the light line is for the best‐fit parameters for the WMAP only fit. The dashed lines assume that the objects with masses greater than 106 M⊙ can form stars. The gray band shows the 68% likelihood region for ﹩z_{r}﹩ based on the assumption of instantaneous complete reionization (Kogut et al. 2003).
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2003. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.