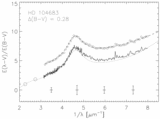
Image Details
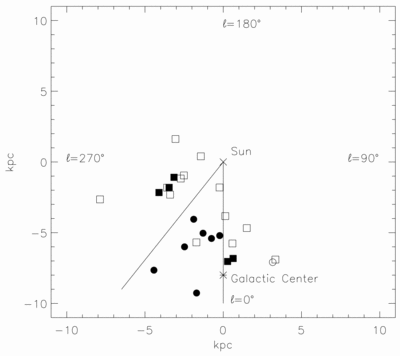
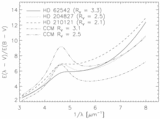
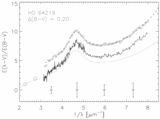
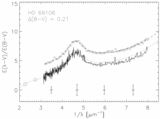
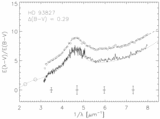
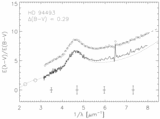
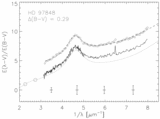
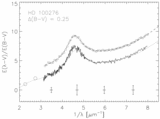
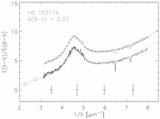
Caption: Fig. 4.
Positions of the stars in our sample in the plane of the Galaxy are plotted with respect to the Sun and the Galactic center. Sight lines marked with circles have weak bumps and steep far‐UV extinction. The sight lines marked with squares have stronger bumps and less extreme far‐UV extinction. Filled circles have ﹩N( \mathrm{Ca}\,\,{}^{{\rm{\small II}}}) / N( \mathrm{Na}\,\,{}^{{\rm{\small I}}}) > 0.62﹩ and ﹩c_{2}> 1.0﹩, open circles have ﹩N( \mathrm{Ca}\,\,{}^{{\rm{\small II}}}) / N( \mathrm{Na}\,\,{}^{{\rm{\small I}}}) < 0.63﹩ and ﹩c_{2}> 1.0﹩, filled squares have ﹩N( \mathrm{Ca}\,\,{}^{{\rm{\small II}}}) / N( \mathrm{Na}\,\,{}^{{\rm{\small I}}}) > 0.62﹩ and ﹩c_{2}< 1.0﹩, and open squares have ﹩N( \mathrm{Ca}\,\,{}^{{\rm{\small II}}}) / N( \mathrm{Na}\,\,{}^{{\rm{\small I}}}) < 0.63﹩ and ﹩c_{2}< 1.0﹩. The wedge represents the SD region where forbidden gas velocities were measured by Sembach & Danks (1994).
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2000. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.