Image Details
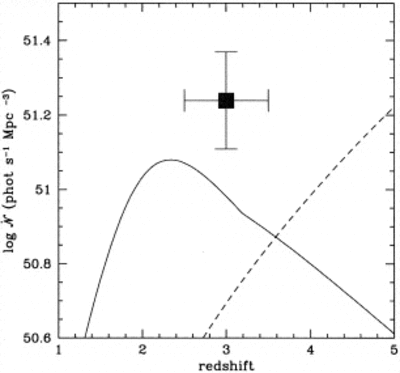
Caption: Fig. 2.
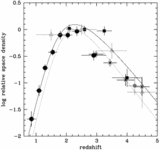
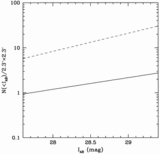
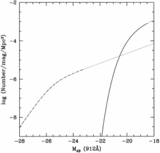
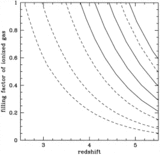
Comoving emission rate of hydrogen Lyman continuum photons (solid line) from QSOs, compared with the minimum rate (dashed line) that is needed to fully ionize a fast recombining Einstein–de Sitter universe with ﹩h_{50}=1﹩, ﹩\Omega _{b}=0.08﹩, and a clumping factor of ﹩C=30﹩. While models based on photoionization by optically selected quasars appear to fall short at ﹩z=5﹩, there are still significant uncertainties (see text for details on the assumed quasar luminosity function and spectral energy distribution). The data point shows the estimated contribution of star‐forming galaxies at ﹩z\approx 3﹩. The fraction of Lyman continuum photons that escapes the galaxy H I layers into the intergalactic medium is taken to be ﹩f_{\mathrm{esc}\,}=0.5﹩.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 1999. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.