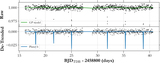
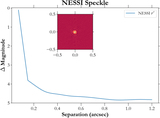
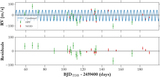
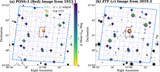
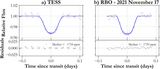
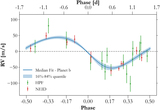
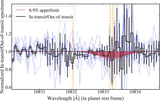
Image Details
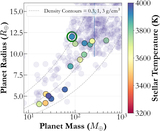
Caption: Figure 10.
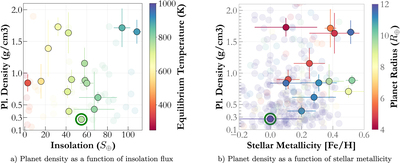
We show the planetary density of gas giants (R p > 4 R ⊕) around M dwarfs (solid colors) as a function of stellar insolation and stellar metallicity, respectively. In panel (a) the markers are color coded by the equilibrium temperature, whereas panel (b) is color coded by planetary radius. Additionally, TOI-3757 b is highlighted with a green circle. In panel (a), we show that TOI-3757 b does not receive an unusually large amount of incident flux from its host star, compared to other similar gas giants. In panel (b), we show that the host star has the lowest metallicity of all known gas giants around M dwarfs, which could be a potential explanation of its density.
Copyright and Terms & Conditions
© 2022. The Author(s). Published by the American Astronomical Society.